
How to Strengthen Security Using CIS Controls and Posture Analysis
How to Strengthen Security Using CIS Controls and Posture Analysis Introduction In the fast-paced and ever-evolving world of cybersecurity, defending digital infrastructure goes far
🔥Premium Monthly Plan – Only $11.99!🔥Hurry! This exclusive deal won’t last long. 👉 Subscribe Now!

How to Strengthen Security Using CIS Controls and Posture Analysis Introduction In the fast-paced and ever-evolving world of cybersecurity, defending digital infrastructure goes far

How to Prepare for the AWS Data Engineer Exam Introduction With the world becoming increasingly data-driven, organizations are depending on cloud-based systems to store, process,

Hybrid vs. Multi-Cloud Transformation: Choosing the Right Strategy for Your Business Introduction In the digital-first economy of today, cloud transformation is no longer a
Table of Contents
 AWS Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3)
AWS Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3)
The most secure, reliable and highly extensible cloud storage is Simple Storage Service (S3). We can easily store and fetch data from anywhere on the web through this object storage with web service. You only need to pay for what you are using in Amazon S3, so in this way, one doesn’t need to worry about capacity and traditional storage space.
It is the foundational web service and the first service introduced by AWS. Most of the applications use Amazon S3 directly or indirectly in AWS.
Amazon S3 can be used with other AWS cloud services because of its high association with other AWS services, or you can use it alone. The most commonly used application is Amazon S3, which is a flexible and highly organized storage.
Typical use cases for Amazon S3 storage include:
For these use cases and many others, Amazon S3 gives a wide range of storage classes for general purpose, unique access, and archive. Its lifecycle helps the data to manage through it; lifecycle policies are configurable in Amazon S3 so that your data will automatically shift to the most suitable storage class without any changing in your code. Amazon S3 provides you with a set of access controls, policies, and encryption to manage the data and who has the right to access your data.
In Amazon S3, we create bucket, store and get back the object and manage permission as well by describing access control and authentication. Access control describes who can access objects and buckets with what type of access (e.g., READ and WRITE). The authentication process performs verification of the identity of a user who is trying to access Amazon Web Services (AWS). Now, we will study Amazon S3 in detail.
 Buckets
BucketsIn Amazon S3, a bucket is a container for storing objects. So, objects are contained in a bucket. S3 Buckets are global, and you can manage them at that level, meaning that any other AWS account cannot use your bucket name because it has to be unique. You can access your bucket by your DNS as well. You can also create multiple buckets. You can upload any amount of objects to the bucket. Each object can contain up to 5 TB of data.
Amazon S3 buckets are global. You can place any bucket in any specific region of your choice to store your data to minimize the cost and to optimize the latency, or you can place it far away from its primary facilities to meet the expectations of any tragedy recovery. Objects never leave their region unless exceptionally transferring those objects to another area or region.
 Objects
Objects
Objects are the fundamental entities stored in Amazon S3. Objects consist of object data, metadata, and unique identifier. The data portion is the actual data that is anything you want to save to Amazon S3. The metadata describes who created that object, what type of info it has, what was the purpose of data that will be used, and many other contextual information.
An identifier is an address through which objects will uniquely be identified within a bucket, through this, we do not need to know the physical location of the object.
 Keys
KeysIn Amazon S3, each object stored in the bucket can be identified by a unique identifier, which is known as Key. A key can be up to 1024 bytes of Unicode including embedded slashes, backslashes, dots, and dashes. Object key uniquely identifies an object in a bucket. A key is unique within the single bucket, but objects with the same key can be obtained in different buckets. The combination of the bucket, key, and version ID uniquely identifies an Amazon S3 object.
Amazon S3 is storage over the internet and objects in Amazon S3 are addressed through a unique URL known as object URL. This URL is created with the help of the combination of a web service endpoint, a bucket name, a key, and optionally, a version.
For example, in the URL http://bucket_ip.s3.amazonaws.com/key.doc, here “bucket_ip” is the bucket name of your choice and “key.doc” is the key.
The Amazon S3 operations are;
Amazon S3 is a flexible system because this data is replicating automatically over multiple servers within the region. Data changing requires some time to forward the changes to all locations. To put new objects is not too difficult because Amazon S3 provides read after write capability but to rewrite over an existing object or delete an object has flexibility. We send PUT request to store data in the bucket and if a PUT request is successful, your data is stored safely. This means when you upload a file and if it is successfully uploaded, then you get HTTP 200 code.
Anyhow, information about the changes must replicate across Amazon S3, which can take some time. Amazon S3 provides;
Eventual Consistency for overwrite PUTS and DELETES can take some time to propagate. If you put up a new object in S3 for the very first time and immediately attempt to read it, you will be able to read it quickly. If the object is replaced or updated then accessed immediately, Amazon S3 might return the prior data until the change is fully propagated.
Amazon S3 provides high levels of data durability and availability by automatically storing the data redundantly across both multiple facilities and multiple devices within the region. There is no chance of failure because of built-in error correction. Amazon S3 standard storage is designed for 99.999999999% durability and 99.99% availability of objects over one year.
You can use Amazon S3 for a static website like html, but Amazon S3 does not host the website that requires databases (e.g., WordPress). This means that Amazon S3 does not support dynamic websites. Static websites are fast, scalable and more secure. To host a static website, you only need to follow the two steps configuration of the bucket and upload the content to a bucket. The URL of website is in this form: <yourbucketname>.s3-website-<AWS-region>.amazon.com.
In S3, you can store a huge amount of data at a negligible cost. You can set policies to migrate your data to Standard – Infrequent Access and Amazon Glacier for archiving to reduce costs further down automatically.
You only pay for the data used with Amazon S3. There are no fixed fee and no installation costs. The S3 Standard Amazon S3 has three pricing components: storage (per month per GB), data-in or -out (per month perGB) as well as requests (per month for 1000 queries). AWS provides the AWS Free Tier to new customers, providing up to five GB of Amazon S3 storage, 20000 GET requests, 2000 PUT requests, and 15 GB of data transfer out each month for one year, all free of cost.
A company has its static website for which it needs a cost effective and quick solution in cloud in an easier way.
By using S3 Static Web Hosting feature, the company can host its website in an easy way with few simple steps.








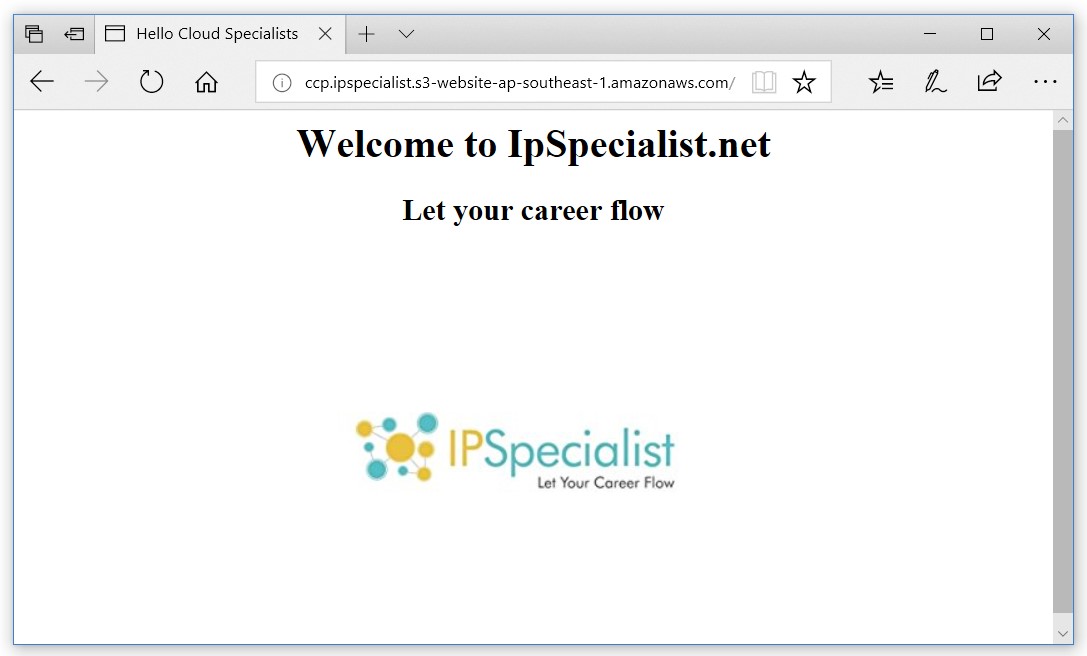

So, in short, we can say that S3 is an extremely cheap, accessible storage option for storing media files, static assets, and user uploads. It is one of the ideal approaches to host your website. You only need to put your HTML, CSS, JS and media files in an S3 bucket and then follow the simple steps to get this website running at very low cost within a couple of minutes. It is quick, cost effective and has incredible uptime. With S3, you also don’t need any capacity planning as it is automatically going up or down, giving you 99.99% availability over a year.
© 2025 All rights reserved | Privacy Policy | Terms and Conditions | Sitemap | Cookie Policy




