
How to Strengthen Security Using CIS Controls and Posture Analysis
How to Strengthen Security Using CIS Controls and Posture Analysis Introduction In the fast-paced and ever-evolving world of cybersecurity, defending digital infrastructure goes far
Master Azure Cloud with IPSpecialist! Gain expert-level skills with our in-depth Azure Courses. Take the next step in your Cloud journey – Start Learning Today!

How to Strengthen Security Using CIS Controls and Posture Analysis Introduction In the fast-paced and ever-evolving world of cybersecurity, defending digital infrastructure goes far

How to Prepare for the AWS Data Engineer Exam Introduction With the world becoming increasingly data-driven, organizations are depending on cloud-based systems to store, process,

Hybrid vs. Multi-Cloud Transformation: Choosing the Right Strategy for Your Business Introduction In the digital-first economy of today, cloud transformation is no longer a
Table of Contents
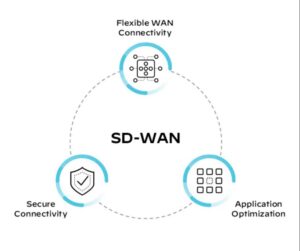
Wide Area Networks (WANs) are managed and optimized for performance using the ideas of Software-Defined Networking (SDN) or SD-WAN (Software-Defined Wide Area Network). It allows businesses to securely link users, applications, and data across numerous sites while enhancing performance, dependability, and scalability. Additionally, SD-WAN makes managing WANs easier by giving centralized control and network visibility. This article covers detailed knowledge of SD-WAN.
By lowering latency, increasing throughput, and enhancing reliability while employing different routes, flexible WAN connectivity enables the optimal use of bandwidth between locations and the data center, all of which assist save costs. Due to this, businesses may use any device or operating system with an internet connection to access their network from anywhere.
Secure connectivity ensures all traffic between sites is encrypted to prevent eavesdropping. This is crucial because any information sent over the internet, even in an email, is susceptible to being intercepted and viewed by a third party who might use it against you or your business.
A crucial part of SD-WAN is application optimization. With this function, you can enhance programs that are delicate to packet loss and delay. Application optimization can help ensure that your calls are always connected and transparent if you use VoIP over the internet.
A virtualized service called SD-WAN expands and links business networks over considerable geographic distances. Users in branch and remote offices can access business applications, services, and resources through Wide Area Networks (WANs), which enable them to work from anywhere by using connectivity, including Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS), wireless, broadband, Virtual Private Networks (VPNs), and the internet. To maintain high speeds and optimize connectivity, SD-WAN keeps track of WAN connection performance and optimizes traffic.
Traditional WANs use antiquated routers to connect remote users to applications hosted in data centers. A router is mainly controlled by a Command Line Interface (CLI). Network engineers and administrators must manually establish rules and policies to specify where and how data exits a branch network using a typical WAN.
The many issues with traditional WAN are intended to be resolved by SD-WAN, giving networking professionals an easier approach to optimize and secure WAN communication. Instead of relying on hardware, SD-WAN is software-based and is set up to manage various traffic patterns and situations in real-time. Compared to traditional WANs, it offers higher security and reliability and can swiftly adapt to changing circumstances.
As traffic is routed through a centralized control plane by SD-WAN, administrators may create rules and policies and instantly deploy them throughout the whole network.
Control is separated from the hardware to streamline network management and improve service delivery. The central SD-WAN controller transmits operational rules to the SD-WAN appliances, which they follow.
As SD-WAN gateways support hybrid WAN, each branch appliance can accommodate numerous connections over various transport methods, including MPLS, high-speed internet, LTE, etc. Each WAN connection often has a virtual private network (VPN) deployed for security.
The network bandwidth, performance, and redundancy are boosted by allowing the WAN to interchangeably employ various connection types (including LTE, MPLS, and broadband internet), enabling centralized control and administration. When operational policies and regulations are disseminated over a complete network simultaneously, separate gateway and router management is significantly reduced or eliminated.
An SD-WAN can be used by companies who prioritize the cloud to improve the application Quality of Experience (QoEx) for consumers. An SD-WAN provides WAN connections with insight while ensuring that apps receive the necessary QoS and security policies.
Secure access to cloud resources is made possible with the highest levels of cloud performance by an active local internet breakout of IaaS and SaaS application traffic from the branch office. Enterprise networks are maintained securely in the process.
Network managers may establish and update security rules in real time as network requirements change because each device is centrally managed, and routing is based on application policies. Organizations can further decrease the complexity, resources, and out-of-pocket expenses needed to set up new locations by integrating SD-WAN with zero-touch provisioning, which helps automate deployment and setup operations.
With SD-WAN, application policies that align with corporate objectives can be automatically provisioned. While continuously monitoring WAN performance, SD-WAN intelligently directs traffic based on Service Level Agreements (SLAs) to preserve application performance. With such a proactive strategy, SD-WAN can restore performance by switching to better WAN links.
Network administrators can scale up or down their WAN connections based on actual demand. Network administrators can use broadband connectivity solutions as a supplement to or a replacement for pricey MPLS. There are fewer ongoing costs for maintenance and support because it is simpler to administer than conventional networks (because it requires less configuration).
Organizations can improve the user experience by enabling adequate access to cloud-based services without backing up traffic to centralized sites. When transferring files or video streams across long distances, static routes are substituted with dynamic ones that adjust to shifting network circumstances in real time with no lag between the source and destination.
You can defend your network from external dangers like DDoS attacks and malware using software-defined networking. Letting only authorized devices onto your network also thwarts internal risks like hacking and data theft. This implies that if someone attempts to access your system from an unauthorized location, they will be automatically stopped.
Your data may remain connected with SD-WAN independent of internet connectivity or geographic location. No matter what happens to their internet or cellular coverage, your employees will always have access to their data.
The adoption of SD-WAN is fueled by the need to quickly and securely connect cloud services and the desire to improve security and lower traditional WAN expenses.
The rising use of containers and cloud-based apps that require access from the edge is one of the developments that are causing SD-WAN solutions to be used more frequently.
Customers increasingly seek SD-WAN technology to connect the data center with cloud resources.
The creation of data source fluidity between on-premises and public cloud will be a key focus. Businesses will continue to extend the use of their own data centers while also increasing the use of public cloud services.
Over the course of more than 20 years, private connectivity has been supported by MPLS technology, from which SD-WAN evolved. SD-WAN can be viewed in many respects as an MPLS software abstraction that works in a larger range of scenarios: It offers cloud-aware, secure connectivity that is private and independent of the type of link or service provider. SD-WAN, like MPLS, manages failure circumstances with real-time traffic redirection based on centralized policies. Furthermore, as SD-WAN unites the whole WAN backbone, it provides thorough analytics across the network internationally. Due to inconsistent infrastructure and policy, this was not possible earlier.
SD-WAN is a valuable technology for modern networking that provides organizations with greater flexibility, agility, and cost savings than traditional WANs. SD-WAN enables businesses to manage their network traffic more efficiently and securely across multiple locations, including branch offices, data centers, and cloud environments.
With SD-WAN, organizations can improve their network performance and reduce downtime by dynamically routing traffic over multiple paths and prioritizing critical applications. SD-WAN also enhances security by providing end-to-end encryption and policy-based access control.
As such, SD-WAN is an important technology for businesses of all sizes and industries, and its adoption is expected to continue to grow as more organizations seek to optimize their network performance and security.
© 2025 All rights reserved | Privacy Policy | Terms and Conditions | Sitemap | Cookie Policy




